Introduction
MongoDB is from “Humongous”
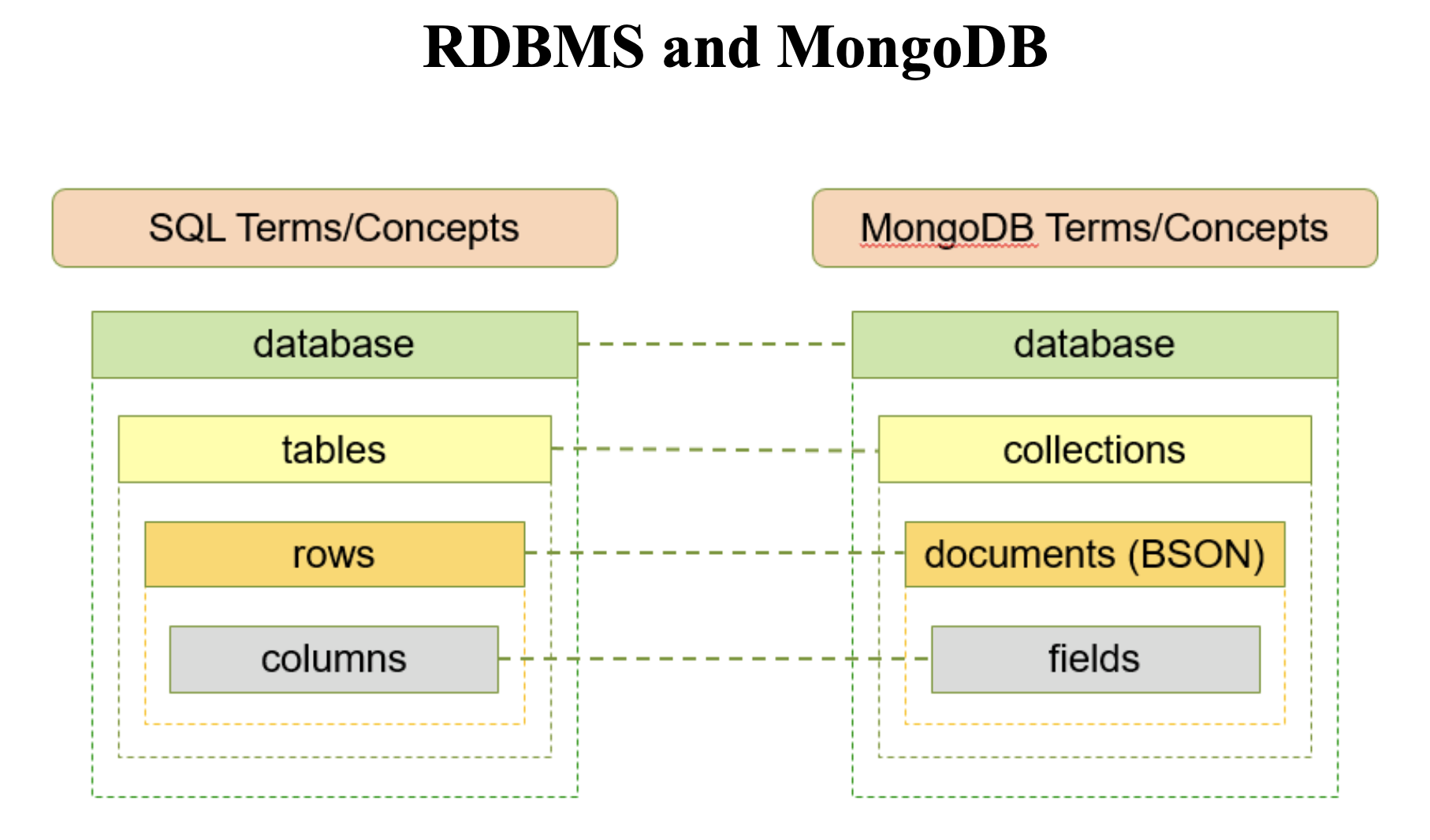
A document-based NoSQL database by MongoDB, Inc.
- Data is stored in documents in JSON.
- Documents of a similar type are stored in collections.
- Related collections are stored in a database.
- Schemaless
Syntactic Rule
- Case-Sensitive – Capitalization matters.
- Semi-colons are not required.
- All string data being saved should be in double quotes.
- Commands are space-independent.
- Comments are indicated by //
- Data is displayed in the order of insertion order.
- The field names cannot start with the $ character.
- The field names cannot contain the . character.
Create a database command – “use”
- e.g. use EmployeeDB
Databases can be displayed by “show dbs” command.
- Admin Database – Records data on database administration issues like users, roles, and privileges for the databases hosted on the server.
- Local Database – Stores data about the server’s start-up process and the server’s role in sharding operations.
- The Admin and Local database will not store any end-user data.
- use method db.getName() to display the database being used.
Create a collection use createCollection() method:
- e.g. db.createCollection(“newproducts”)
Collections can be displayed by “show collections” command.
Dropping a collection use drop()
e.g.
- Removes the collection “newproducts” along with all its documents: db.newproducts.drop()
- Delete all the documents in the collection: db.newproducts.remove({})
- Rename collections, use the method renameCollection()
Common Term in MongoDB
Field: key-value pair in a document
_id:
- mandatory field for every document. If you don;t assign a value, system will assign a random value this it.
- serves as primary key.
- unique valye in the collection
CRUD
Create
- db.collection.insert(document)
- db.collection.insertOne(document)
- db.collection.insertMany([{d1}, {d2}.., {d3}] )
- db.collection.save(document)
- db.collection.update(query ,update , { upsert: true } )
Read
- db.collection.find( query, projection )
- db.collection.findOne(query, projection )
Update
- db.collection.update(query ,update, options)
- db.collection.updateOne(query ,update, options)
- db.collection.updateMany(query ,update, options)
- db.collection.replaceOne(query ,replacement, options)
Delete
- db.collection.remove(query, justOne)
- db.collection.deleteOne( query, options)
- db.collection.deleteMany( query, options )
- db.collection.deleteMany({}) // delete all documents
Installation
Download & unzip source code to cd /usr/local
Rename directory to mongodb
Add to PATH
1
export PATH=/usr/local/mongodb/bin:$PATH
Create a database directory
1
2sudo mkdir -p /data/db
sudo chown -R $USER /data/dbRun mongodb
1
2
3
4sudo mongod
# if doesn't set PATH, entry the following directory
cd /usr/local/mongodb/bin
sudo ./mongodOpen another terminal:
1
2$ cd /usr/local/mongodb/bin
$ ./mongoif your data directory not /data/db, assign it with —dbpath
1
sudo mongod --dbpath = /data/db
Practice
Basic Manipulation
Create a collection called “customers”, input data
1
2
3
4db.customers.insert({id: "1", name : "Bill", productId: "1", customerId: "1", amount: 20.00, state: "PA"})
db.customers.insert({id: "2", name : "Hillary", productId: "2", customerId: "2", amount: 30.00, state: "DC"})
db.customers.insert({id: "3", name : "brian", productId: "1", customerId: "3", amount: 25.00, state: "DC"})
db.customers.insert({id: "4", name : "Donald", productId: "2", customerId: "4", amount: 50.00, state: "PA"})Find the name and amount of all the customers whose state is PA
1
db.customers.find({ state: "PA" }, { name: 1, _id: 0 })
Find the name and state of customers whose name begin with “B” or “b”
1
db.customers.find({ name: /^(B|b)/ })
Find the name of customers whose sale amount is greater or equal to 30 but lower than 40
1
db.customers.find( { amount: { $gte: 30, $lt: 40 } } )
For each state, find the number of customers and their total amount
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8db.customers.aggregate( [
{ $group: {
_id: "$state",
total_amount: { $sum: "$amount" },
num_of_customers: { $sum: 1 }
}
}
] )To all the documents, increase the salesAmount by 10
1
db.customers.updateMany( {}, { $inc: { "amount": 10 } } )
To all the documents, add the new field called “totalSaleAmount” whose value is defined by saleAmount*1.06 (i.e, add 6% tax)
1
db.customers.aggregate( [ {$addFields: {totalSaleAmount: {$multiply: ["$amount", 1.06] } } } ] )
To all the documents whose state is PA, add the new field called “pastPurchase” as an array of products. Document 1 will have [“chair”, “desk”], while Document 4 will have [“chair”, “tablet”, “usb”]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8db.customers.update(
{ id : "1" },
{ $set: { "pastPurchase" : ["chair", "desk"] } }
)
db.customers.update(
{ id : "4" },
{ $set: { "pastPurchase" : ["chair", "tablet", "usb"] } }
)
MapReduce Implementation
We need to find some aggregated data from a Grocery Store (Giant, ACME etc.,) by their shoppingCarts. The document structure is:
1 | { |
Input data
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9db.grocery.insert({name: "Bob", shoppingCart: "Milk, Corn, Chocolates", discount: 0.75});
db.grocery.insert({name: "Alice", shoppingCart: "Milk, Turkey, Apple", discount: 0});
db.grocery.insert({name: "Trudy", shoppingCart: "Cheese, Corn, Tomatoes, Ginger, Juice, Pork", discount: 1.50});
db.grocery.insert({name: "Jacob”, shoppingCart: "Ice Cream, Onions, Tomatoes, Vinegar, Chicken, Fish", discount: 2.60});
db.grocery.insert({name: "Paul", shoppingCart: "Cheese, Chocolates, Fish, Bread"});
db.grocery.insert({name: "Jack", shoppingCart: "Milk, Corn, Fish", discount: 0.25});
db.grocery.insert({name: "Mary", shoppingCart: "Milk, Turkey, Apple", discount: 0});
db.grocery.insert({name: "Kate", shoppingCart: "Cheese, Apple, Corn, Juice, Pork", discount: 3.50});
db.grocery.insert({name: "Chris", shoppingCart: "Ice Cream"});Add the fact that you purchased the following items {Apple, Ice Cream, Chocolates} with the discount of $1.25. That is, use your first name as the name of the new document
1
db.grocery.insert({name: "Celine", shoppingCart: "Milk, Corn, Chocolates", discount: 1.25});
Use Map/Reduce function to count all the people who got any discount at all. Show the complete code and output
1
db.grocery.find().pretty()
Use Map/Reduce function to count all the people who got any discount at all. Show the complete code and output
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11db.grocery.mapReduce(
function() {
if(this.discount != undefined && this.discount > 0){
emit("count", 1);
}
}, // mapper
function(key,values) {
return Array.sum(values);
}, // reducer
{ out: "discounts" } // output
).find();
Use Map/Reduce function to count the total value of discounts of all the customers. Show the complete code and output
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11db.grocery.mapReduce(
function() {
if(this.discount != undefined && this.discount > 0){
emit("sum",this.discount);
}
}, // mapper
function(key,values) {
return Array.sum(values);
}, // reducer
{ out: "discounts" } // output
).find();Use Map/Reduce function to find the number of times an item appears in the cart.
For example, if Chicken was inserted in 5 documents (5 different Carts), the key value pair generated after map reduce should look like: {Chicken: 5}
Display the top 5 items most sold:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15db.grocery.mapReduce(
function() {
if(this.shoppingCart != undefined) {
this.shoppingCart.split(',').forEach(
function (v) {
emit(v.trim(), 1);
}
);
}
},
function(key,values) {
return Array.sum(values);
},
{ out: "top5Sellers" }
).find().sort({value: -1}).limit(5);