NoSQL = Not Only SQL
ACID - Atomic, Consistent, Isolated, Durable
BASE - Basic Availability, Soft-state, Eventual consistency
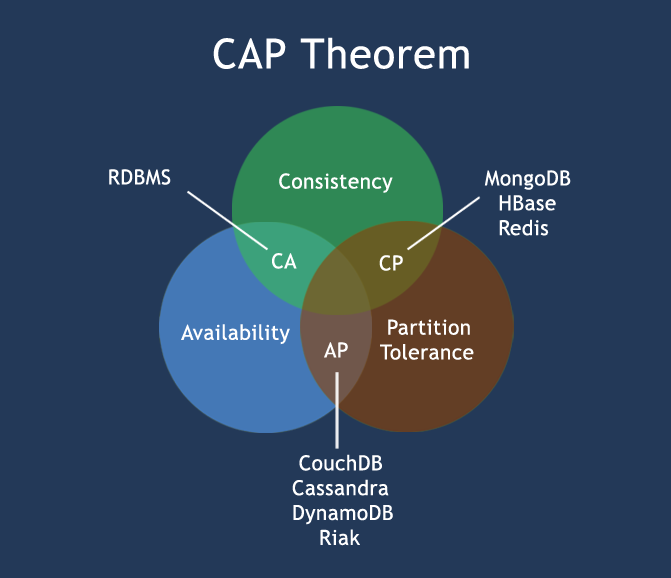
CAP Theroem
- Consistency: Every read receives the most recent value
- Availability: Every request receives a (non-error) response without the guarantee that it contains the most recent write. no downtime.
- Partition Tolerance: The system continues to operate despite an arbitrary number of nodes being dropped.
NoSQL Database
| Key-value Store | Column Store | Document Store | Graph Store | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Usage | - image stores - Key-tased file systems - Object cache - System designed to scale |
- Web crawler results - Big data problem with relaxed consistency riles |
- High variability data - Document search - Web content management - Publishing |
- Social network - Fraud detection - Relationship heavy data |
| Example | Memcache Redis Riak | Hbase Cassandra Hypertable | MongoDB CoutchDB CouchBase | Neo4J InfinteGraph(Objectively) |
NoSQL Models: Key/Value Systems
- A store of two fields: (Key, Value) pairs.
- Only one way to access the data through hashing(Key) = value
- No query language: only get/put/delete/update
- Limited multi-record transactional consistency
- Each row has timestemp
API
- lookup(key) -> value
- lookup(key range) -> value
- getNext -> value
- insert(key, value)
- delete(key)
Use Cases
- Storing data for customer preferences and profiles
- Customized product recommendations, Ads, coupons
- User profiles
- Using cache to accelerate application responses
- As a cache for heavily accessed but rarely updated data
NoSQL Models: Column Store
- Motivated by Google’s BigTable
- Extension of the K/V system, where columns can have a complex structure, rather than a blob value
- Supports complex modeling structure (nested tables, repeating groups, set, list, etc.)
- Big Table, Cassandra, HBase, Vertica, Accumulo, Hypertable, etc
NoSQL Models: Document Store
- Similar to Key-value store, but the value is a complete document, such as JSON, XML, etc.
- Any collection of documents such as maps, collections, and scalar values.
NoSQL Models: Graph Databases
- Models data in terms of nodes and connections
- Useful for inter-connected data such as communication patterns, social networks, bio interactions.
- Allows us to ask deeper and more complex questions
- Difficult to distribute components of a graph among a network of servers as graphs become larger.
Summary
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| - Utilize the scale-out architecture that supports scalability, fault tolerance, and high availability - Rapid insertion of arbitrary heterogeneous data with schema-on-read - High performance of sequential scan (good for batch-oriented job such as OLAP workload) |
- Lack of ACID - Not adequate for OLTP workload that requires random access and ACID - Lack of high-level functionality such as SQL, schemas, and secondary indexes |